词典 Dictionary
|
1. 词典 Dictionary 定义 词典,也称映射(map),表(table)或关联数组(associatearray),词典中每个元素都由两部分组成:一个关键字,通常称为查找键(search key);一个与该键值相关联的值。 词典根据查找键来组织与区分它的元素,因此只要指定元素的查找键,就能从词典中检索或删除一个元素。词典中每个元素都具有一个查找键,虽然也可以将具有查找键的元素放入线性表,但线性表的数据是按位置而不是按查找键来组织的。 Java接口 public interface DictionaryInterface<K, V> {
/**
* 将一个新元素插入词典。如果给定的查找键一再词典中,则替换相应的值
* @param key 新元素的查找键对象
* @param value 与查找键相关联的对象
* @return 如果新元素被插入到词典中则返回null,如果与key相关联的值被替换,则返回原来的值 */
public V add(K key, V value);
/**
* 从词典中删除一个指定的元素
* @param key 欲删除的元素的查找键对象
* @return 与查找键相关联的值,如果不存在这样的对象则返回null */
public V remove(K key);
/**
* 检索与给定的查找键相关联的对值
* @param key 欲检索的元素的查找键对象
* @return 与查找键相关联的值,如果不存在这样的对象则返回null */
public V getValue(K key);
/**
* 确定一个指定的元素在不在词典中
* @param key 欲检索的元素的查找键对象
* @return 如果key与词典中的一个元素相关联则返回true */
public boolean contains(K key);
/**
* 创建一个迭代器遍历词典中所有的查找键
* @return 返回一个迭代器,提供对词典中查找键的顺序访问 */
public Iterator<K> getKeyIterator();
/**
* 创建一个迭代器遍历词典中所有的值
* @return 返回一个迭代器,提供对词典中的值顺序访问 */
public Iterator<V> getValueIterator();
/**
* 确定词典是否为空
* @return 如果词典为空则返回true */
public boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 确定词典是否为满
* @return 如果词典为满则返回true */
public boolean isFull();
/**
* 缺德词典的大小
* @return 返回词典中当前的元素(键-值二元组)数目 */
public int getSize();
/**
* 删除词典中所有元素 */
public void clear();
}Java类库:Map接口 public interface Map<K, V> {
public V put(K key, V value);
public V remove(Object key);
public V get(Object key);
public boolean containsKey(Object key);
public boolean containsValue(Object value);
public Set keySet();
public Collection<V> values();
public boolean isEmpty();
public int size();
public void clear();
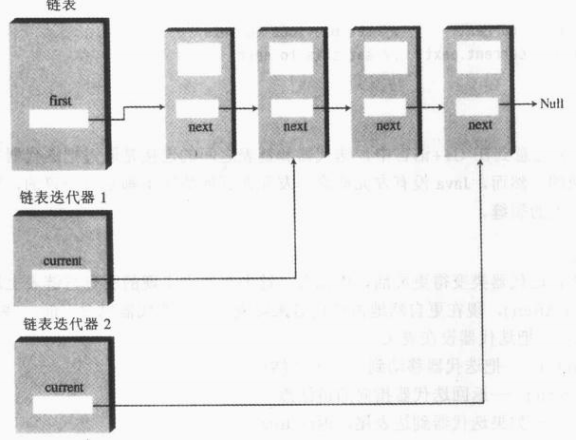
}2. 迭代器 Iterator 迭代器总是指向链表中的一些链接点。它同链表相关联,但并不等同于链表或链接点。
迭代器类 迭代器类包含对数据结构中数据项的引用,并用来遍历这些结构的对象。 public class Link {
public long dData;
public Link next;
}
public class LinkList {
private Link first;
public ListIterator getIterator() {
return new ListIterator(this);
}
}
public class ListIterator {
private Link current; // reference to current link
private Link previous; // reference to previous link
private LinkList ourList; // reference to "parent" list
public ListIterator(LinkList list) {
ourList = list;
reset();
}
// 把迭代器复位并设在表头
public void reset() {
current = ourList.getFirst();
previous = null;
}
public boolean atEnd() {
return (current.next == null);
}
public void nextLink() {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
public Link getCurrent() {
return current;
}
// 在当前链接点前插入新连接点
public void insertAfter() {
Link newLink = new Link();
if (ourList.isEmpty()) {
ourList.setFirst(newLink);
current = newLink;
} else {
newLink.next = current.next;
current.next = newLink;
nextLink();
}
}
// 在当前链接点后插入新连接点
public void insertBefor() {
Link newLink = new Link();
if (previous == null) {
newLink.next = ourList.getFirst();
ourList.setFirst(newLink);
reset();
} else {
newLink.next = previous.next;
previous.next = newLink;
current = newLink;
}
}
// 删除当前链接点
public long deleteCurrent() {
long value = current.dData;
if (previous == null) {
ourList.setFirst(current.next);
reset();
} else {
previous.next = current.next;
if (atEnd())
reset();
else
current = current.next;
}
return value;
}
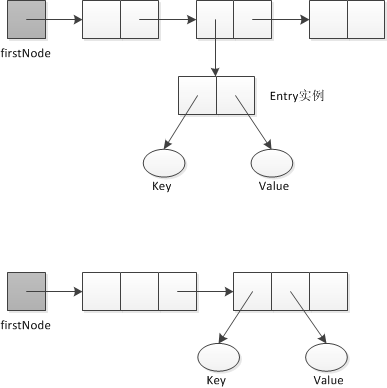
}3. 基于数组实现词典 词典中的每个元素必须是Entry类的一个实例。
基于数组的无序词典 public class ArrayDictionary<K, V> implements DictionaryInterface<K, V>,
Serializable {
private Entry<K, V>[] dictionary; // 无需元素的数组
private int currentSize; // 元素的数量
private final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 25;
public ArrayDictionary() {
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
public ArrayDictionary(int initialCapacity) {
// 编译器发现,含有Entry类型的元素的数组赋给了含有Entry<K,V>类型的元素的数组。因此,它警告有一个未检验的转换。
// 试图把新数值转换为Entry<K,V>也将导致一个类似的警告。
// 这两种情况都不用编译器的警告。
dictionary = new Entry[initialCapacity];
currentSize = 0;
}
private class Entry<S, T> implements Serializable {
private S key;
private T value;
private Entry(S searchKey, T dataValue) {
key = searchKey;
value = dataValue;
}
// 内部Entry不具有用于设置或修改查找键的方法setKey
public S getKey() {
return key;
}
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public V add(K key, V value) {
// 讲一个新的键-值元素插入词典并返回null。如果key已在词典中,则返回相应的值,并且用value替换它
V result = null;
// 在数值中查找含有key的元素
int keyIndex = locateIndex(key);
// 如果在数组中找到含有key的元素
if(keyIndex < currentSize) {
// result = 当前与key相关联的值
result = dictionary[keyIndex].getValue();
// 以value替换与key相关联的值
dictionary[keyIndex].setValue(value);
} else {
// 数组已满
if(isArrayFull())
// 将其长度加倍
doubleArray();
// 为由当前的查找确定的索引处的新元素在数组中腾出空间,江汉油田key与value的新元素插入数组中空出的位置
dictionary[currentSize] = new Entry<K, V>(key, value);
// 词典长度加1
currentSize++;
}
return result;
}
// 返回含有查找键的元素的索引,或者如果元素不存在,返回currentSize
private int locateIndex(K key) {
int index = 0;
while((index < currentSize) && !key.equals(dictionary[index].getKey()))
index++;
return index;
}
public V remove(K key) {
// 给定查找键,从词典中删除一个元素,并返回该元素的值。如果不存在这样一个元素,则返回null
V result = null;
// 在数组中查找含有给定查找键的元素
int keyIndex = locateIndex(key);
// 在词典中找到了含有给定查找键的元素
if(keyIndex < currentSize) {
// result = 当前与key相关联的值
result = dictionary[keyIndex].getValue();
// 用数组的最后一个元素替换该元素
dictionary[keyIndex] = dictionary[currentSize -1];
// 词典长度减1
currentSize --;
}
return result;
}
}基于数组的有序词典 public class SortedArrayDictionary<K extends Comparable<? super K>, V>
implements DictionaryInterface<K, V>, Serializable {
private Entry<K, V>[] dictionary; // 无需元素的数组
private int currentSize; // 元素的数量
private final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 25;
public SortedArrayDictionary() {
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
public SortedArrayDictionary(int initialCapacity) {
// 编译器发现,含有Entry类型的元素的数组赋给了含有Entry<K,V>类型的元素的数组。因此,它警告有一个未检验的转换。
// 试图把新数值转换为Entry<K,V>也将导致一个类似的警告。
// 这两种情况都不用编译器的警告。
dictionary = new Entry[initialCapacity];
currentSize = 0;
}
public V add(K key, V value) {
// 讲一个新的键-值元素插入词典并返回null。如果key已在词典中,则返回相应的值,并且用value替换它
V result = null;
// 查找数组,直到发现含有key的元素,或者找到这样的元素应处的位置
int keyIndex = locateIndex(key);
// key已在词典中
if((keyIndex < currentSize) && key.equals(dictionary[keyIndex].getKey())) {
// result = 当前与key相关联的值
result = dictionary[keyIndex].getValue();
// 以value替换与key相关联的值
dictionary[keyIndex].setValue(value);
} else { // 插入新元素
// 数组已满
if(isArrayFull())
// 将其长度加倍
doubleArray();
// 移动数组元素,在指定索引处为新元素腾出空间
makeRoom(keyIndex);
// 为由前面的查找确定的索引处的新元素在数组中腾出位置,将含有key与value的新元素插入到数组中空出的位置
dictionary[currentSize] = new Entry<K, V>(key, value);
// 词典长度加1
currentSize++;
}
return result;
}
// 返回含有查找键的元素的索引,或者如果元素不存在,返回currentSize
private int locateIndex(K key) {
// 进行查找,知道找到一个含有key的元素,或传递它应在的位置
int index = 0;
while((index < currentSize) && key.compareTo(dictionary[index].getKey())> 0)
index++;
return index;
}
}4. 基于链表实现词典 使用链表的另一种选择时不使用Entry类。简单的方式是修改节点的定义,使之包含元素的两个部分。
基于链表的无序词典 由于无序词典中的元素没有特定的顺序,所以可用最有效的方法来插入新元素。如果元素是用链表来存放的,则最快的插入方法就是在链表的始端进行插入,插入的效率是O(1)。 基于链表的有序词典
public class SortedLinkedDictionary<K extends Comparable<? super K>, V>
implements DictionaryInterface<K, V>, Serializable {
private Node firstNode; // 指向链表的第一个结点的引用
private int currentSize; // 元素的数量
public SortedLinkedDictionary() {
firstNode = null;
currentSize = 0;
}
private class Node<K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> implements Serializable {
private K key;
private V value;
private Node next;
}
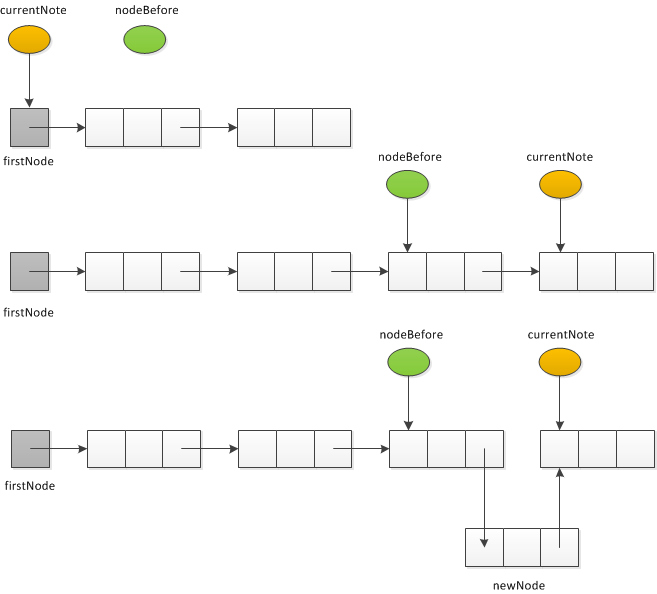
public V add(K key, V value) {
// 将一个新的键-值元素插入词典并返回null。如果key已在词典中,则返回相应的值,并且用value替换它
V result = null;
// 查找链表,直到找到一个含有key的结点,或者传递它应在的位置
Node currentNode = firstNode;
Node nodeBefore = null;
while((currentNode != null) && key.compareTo(currentNode.getKey()) > 0) {
nodeBefore = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.getNext();
}
// 包含key的结点在链表中
if((currentNode != null) && key.equals(currentNode.getKey())) {
// result = 当前与key相关联的值
result = currentNode.getValue();
// 用value替换与key相关联的值
currentNode.setValue(value);
} else { // 链表为空,或者新元素应位于链表始端
// 为包含key和value的新结点分配存储空间,为该新结点插入到链表始端
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
// 词典长度加1
currentSize++;
if(nodeBefore == null) {
// 在开头插入
newNode.setNext(firstNode);
firstNode = newNode;
} else {
newNode.setNext(currentNode);
nodeBefore.setNext(newNode);
}
}
return result;
}
}
转载请并标注: “本文转载自 linkedkeeper.com ” ©著作权归作者所有 |